XML file formats
A simple XML format can used to store RiskTrees as mind maps, for sharing with other applications.
By default, the latest version of RiskTree loads, stores, and saves RiskTrees in JSON format.
RiskTree continues to support the MindMap XML format, which is a standard output from many commercially
available mind mapping tools. The data structure is very simple, and based around the <node> tag. The information in the node is
held in a TEXT attribute.
Each child node has a <node> tag nested within its parent <node> tag. This nesting continues until an end node
is reached; here, a closed <node /> tag is used. To reverse back up the tree, closing </node> tags are used.
Assessment values are placed into the end nodes separated by forward slashes. They need to be separate from the node name by a line feed character, which
is encoded in XML as . These XML tags also need to be closed, which is most easily achieved by including a final forward slash before
the closing angle bracket. This is best demonstrated by an example:
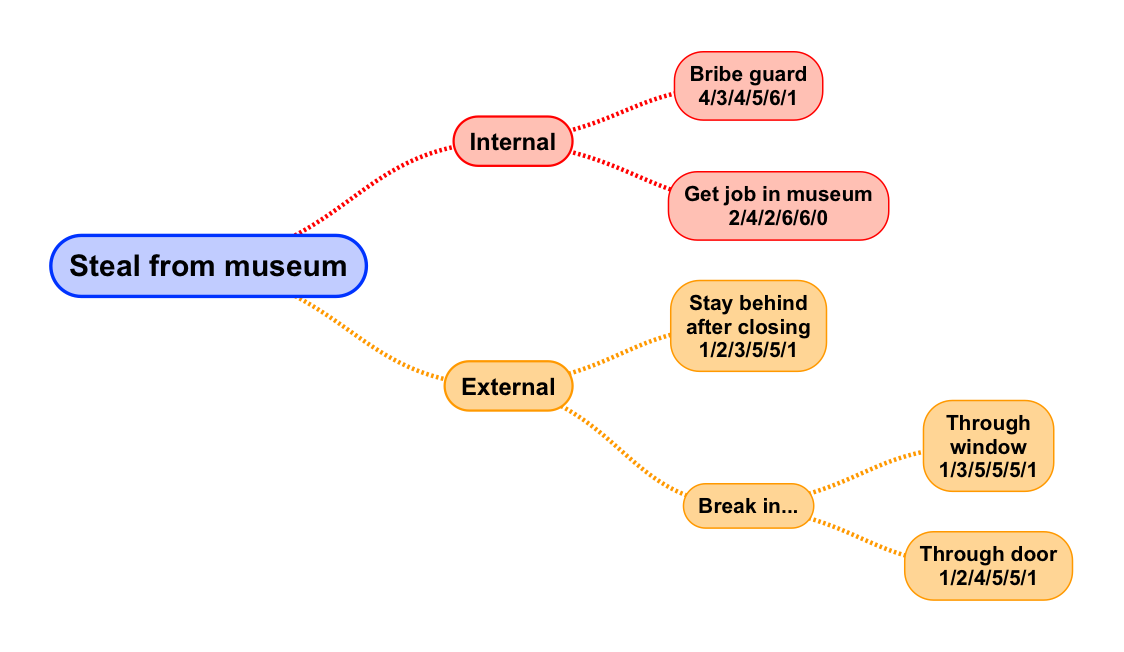
The XML for this attack tree looks like this:
<map version="0.9.0">
<node text="Steal from museum">
<node text="Internal">
<node text="Bribe guard 4/3/4/5/6/1" />
<node text="Get job in museum 2/4/2/6/6/0" />
</node>
<node text="External">
<node text="Stay behind after closing 1/2/3/5/5/1" />
<node text="Break in...">
<node text="Through window 1/3/5/5/5/1" />
<node text="Through door 1/2/4/5/5/1" />
</node>
</node>
</node>
</map>
The indentation, using tabs, is not required. It is used in this example to make the nesting of the <node> tags easier to see. For example, the three </node>
tags at the end of the file close, respectively, the Break in..., External, and Steal from museum nodes.